Oral health plays a vital role in a child’s overall well-being and development, and it’s never too early to prioritize it. Pediatric dental issues are common, but many of them can be prevented or minimized with the right care. From early decay to developing habits that could impact oral alignment, understanding these common issues can help parents and caregivers support their child’s dental health from a young age. Here’s a look at some of the most frequent pediatric dental issues and effective prevention tips to keep children’s smiles healthy and bright.
1. Tooth Decay (Cavities)
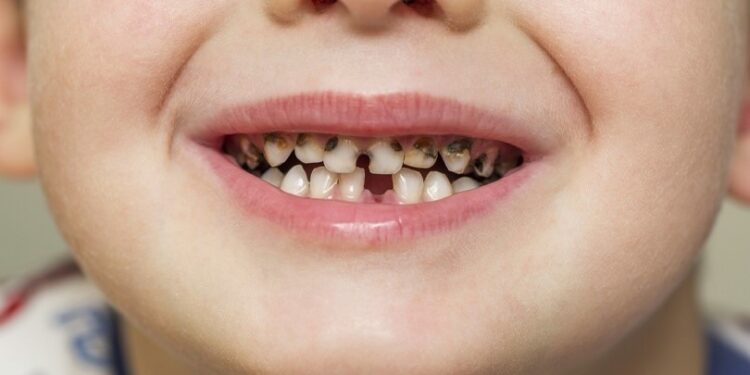
Tooth decay, also known as cavities, is the most prevalent chronic condition among children. It occurs when bacteria in the mouth feed on sugars from food and beverages, producing acid that erodes tooth enamel. Baby teeth are more susceptible to decay due to their softer enamel.
Prevention Tips:
- Establish a Dental Hygiene Routine: Start brushing your child’s teeth as soon as they appear with a soft, small-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste.
- Limit Sugary Snacks and Drinks: Encourage water over sugary juices or sodas and limit sweets, which can lead to acid buildup on teeth.
- Visit the Dentist Early: The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry (AAPD) recommends a dental visit by age one, allowing a dentist to catch any early signs of decay.
- Use Fluoride: Fluoride strengthens enamel, making it more resistant to decay. Many communities add fluoride to tap water, but if yours doesn’t, ask your dentist about fluoride supplements or treatments.
2. Thumb Sucking and Pacifier Use
Thumb sucking and pacifier use are normal in infants and toddlers, but prolonged habits can impact tooth alignment and jaw development. This can lead to open bites, crossbites, or other alignment issues if the habit persists as permanent teeth start to come in.
Prevention Tips:
- Limit Pacifier Use: Encourage stopping pacifier use by age two to reduce risks of alignment issues.
- Encourage Positive Alternatives: Distract children with toys or activities to minimize thumb-sucking when they’re feeling bored or anxious.
- Reward Systems: For older children who continue thumb-sucking, create a gentle reward system to encourage them to stop, focusing on positive reinforcement.
3. Early Tooth Loss
Losing baby teeth too early, often due to decay or injury, can cause alignment problems for incoming permanent teeth. When a baby tooth is lost prematurely, the surrounding teeth may shift, leading to crowding or improper eruption of adult teeth.
Prevention Tips:
- Encourage Protective Habits: Ensure children wear mouthguards during sports activities to prevent injury to teeth.
- Practice Good Oral Hygiene: Regular brushing and flossing, along with dentist visits, help keep baby teeth healthy and reduce the risk of early tooth loss due to decay.
- Consult with a Dentist: If a baby tooth is lost too early, a dentist may recommend a space maintainer to keep surrounding teeth in place until the adult tooth emerges.
4. Gum Disease (Gingivitis)
Gum disease isn’t limited to adults; children can also develop gingivitis due to poor oral hygiene. Symptoms include red, swollen, or bleeding gums, often caused by the buildup of plaque around the gum line.
Prevention Tips:
- Regular Brushing and Flossing: Teach children to brush twice a day and floss daily to prevent plaque buildup along the gums.
- Use a Kid-Friendly Mouthwash: Many mouthwashes are available in child-friendly flavors and are effective in reducing plaque and bacteria.
- Routine Dental Cleanings: Regular professional cleanings help prevent gum disease by removing plaque and tartar that at-home brushing may miss.
5. Tooth Sensitivity
Children may experience tooth sensitivity due to several factors, such as enamel erosion, cavities, or new teeth erupting. Sensitive teeth can make eating and drinking uncomfortable, and if left unaddressed, may discourage children from proper brushing habits.
Prevention Tips:
- Avoid Acidic Foods: Limit acidic foods and drinks like citrus fruits and sodas, which can erode enamel.
- Use a Soft-Bristled Brush: Hard bristles can wear down enamel, so ensure children use a soft-bristled toothbrush and brush gently.
- Check with the Dentist: Persistent sensitivity may indicate a cavity or other issue, so consult a dentist for a proper diagnosis.
6. Malocclusion (Misaligned Bite)
Malocclusion refers to misalignment of the teeth and jaw, which can occur due to genetics, prolonged thumb sucking, early tooth loss, or injuries. Issues like crowding, overbites, or crossbites can impact a child’s ability to chew, speak, and even clean their teeth effectively.
Prevention Tips:
- Encourage Early Orthodontic Evaluations: The AAPD suggests an orthodontic evaluation by age seven. Identifying malocclusion early on can help prevent more extensive treatment later.
- Discourage Prolonged Habits: As with thumb sucking, pacifiers, and other oral habits, early intervention is key to preventing alignment issues.
- Practice Good Oral Hygiene: Keeping teeth healthy prevents early loss or decay that can contribute to malocclusion.
7. Dental Anxiety
Dental anxiety is a common issue that can lead to skipped appointments and poor oral hygiene practices. Addressing dental anxiety early helps children feel comfortable and encourages lifelong oral care.
Prevention Tips:
- Choose a Pediatric Dentist: Pediatric dentists Fort Mill SC are trained to work with children and create a welcoming, kid-friendly environment.
- Use Positive Reinforcement: Praise children for good behavior at the dentist and reward them afterward to build positive associations.
- Explain the Process: Talk to children about what to expect during a visit. Reading books or watching age-appropriate videos about dental visits can help demystify the experience.
8. Dental Trauma and Injuries
Active children are often at risk for dental trauma, whether from sports or playground accidents. Broken, chipped, or knocked-out teeth are common and can have lasting effects if not treated promptly.
Prevention Tips:
- Wear Mouthguards: A properly fitted mouthguard is essential for children involved in contact sports to protect against tooth injuries.
- Teach Safe Play Practices: Encourage safe play and supervise activities to minimize the risk of falls or collisions.
- Seek Immediate Care: If a tooth injury occurs, contact a dentist right away. Immediate care can often save a tooth or prevent further complications.
Conclusion: Building Good Habits for Lifelong Oral Health
Most pediatric dental issues are preventable with early intervention, proper education, and consistent oral hygiene practices. By teaching children to care for their teeth and gums, encouraging regular dental visits, and addressing any habits or behaviors that may lead to problems, parents can lay the foundation for lifelong dental health. Investing in prevention not only helps children avoid common dental issues but also encourages a lifetime of confidence in their smile.